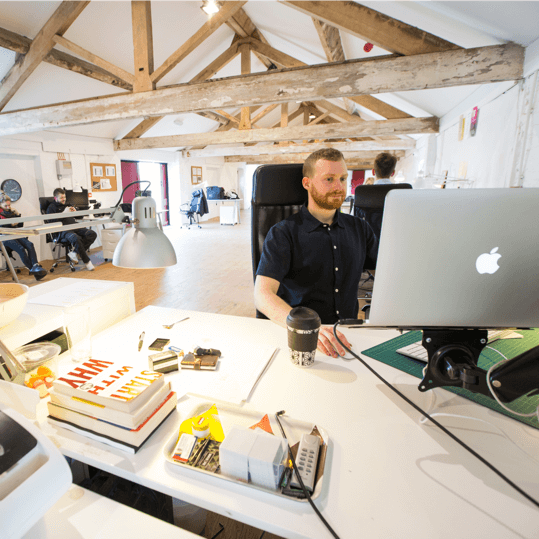
In today’s digital-first world, businesses must choose how they want to reach and engage their users—through native mobile apps or web apps. Both approaches have their advantages, but when it comes to user experience, native apps consistently outperform web apps. With the rapid growth of smartphones and evolving expectations for speed, personalization, and functionality, businesses looking to stand out should strongly consider mobile app development as part of their digital strategy.
This article explores why native apps provide a superior user experience compared to web apps, and how thoughtful web design, web development, and mobile app development can transform customer engagement.
1. Performance and Speed
One of the key reasons native apps deliver a better experience is performance. Native apps are developed specifically for a particular operating system, such as iOS or Android, which allows them to directly leverage the device’s hardware and software features. This results in:
Faster loading times
Smooth navigation
Minimal crashes or glitches
On the other hand, web apps are limited by the browser they run in. Even with the best web development practices, web apps often struggle to match the responsiveness of native apps. Users today expect instant interactions; if your app takes more than a few seconds to load, you risk losing them.
2. Seamless Integration with Device Features
Native apps provide deeper integration with mobile devices. They can access and utilize device-specific features like:
Camera
GPS
Push notifications
Contacts and calendar
Biometrics (fingerprint or face recognition)
This integration enhances functionality and makes the user journey smoother. For example, a fitness tracking app can use a phone’s accelerometer and GPS to track steps and routes in real time—something web apps can’t replicate with the same efficiency.
With mobile app development, businesses can tap into these features to offer tailored, immersive experiences that web apps simply cannot achieve.
3. Offline Accessibility
Native apps also have the advantage of working offline or with limited connectivity. Data can be stored locally, so users can still access essential features without needing an internet connection.
Think of note-taking apps, language learning platforms, or even e-commerce apps that allow browsing offline. This capability creates convenience and reliability—two critical aspects of user experience.
Web apps, in contrast, rely heavily on internet access. Even with progressive web development methods like Progressive Web Apps (PWAs), their offline capabilities remain limited.
4. Personalization and User Engagement
Today’s customers expect personalized experiences. Native apps allow developers to create customized user journeys based on preferences, behaviors, and demographics. Features like:
Personalized push notifications
Tailored content feeds
In-app recommendations
… all contribute to stronger engagement.
Push notifications, in particular, are one of the most powerful engagement tools available. With native apps, businesses can send timely reminders, promotions, or updates directly to a user’s device. This helps build stronger relationships and improves retention rates.
While web apps can offer some personalization through cookies and browsing data, they lack the same direct communication channels and immersive engagement tools.
5. Security and Trust
Security is a top concern for both businesses and users. Native apps are built with operating system security protocols and can leverage advanced features like biometric authentication and encrypted storage.
For industries like finance, healthcare, and e-commerce, this level of trust is invaluable. While good web design and web development can certainly improve security for web apps, native apps benefit from stronger built-in protections provided by the platform.
6. Enhanced User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX)
Great web design is about simplicity, clarity, and functionality, but native apps take this to another level. Because they are tailored for specific platforms, native apps follow the design guidelines of iOS and Android. This ensures that users experience familiar interfaces, gestures, and interactions, making navigation intuitive.
Animations, transitions, and layouts in native apps feel smoother compared to web apps. This attention to design details enhances user satisfaction and creates a sense of brand professionalism.
7. Scalability and Long-Term Value
When businesses invest in mobile app development, they’re building a scalable platform that can grow with them. Native apps can be updated regularly with new features, bug fixes, and design improvements. App stores also provide a structured environment for version control and distribution.
Web apps, while easier to update across platforms, often face compatibility issues with different browsers and devices. This can complicate scaling and result in inconsistent user experiences.
8. Brand Visibility and Customer Loyalty
Publishing a native app on the Apple App Store or Google Play Store enhances brand visibility. Having your brand represented in these trusted marketplaces builds credibility and puts your app directly in front of millions of users searching for solutions.
Native apps also encourage customer loyalty by becoming part of the user’s daily routine. An app icon on the home screen is a constant reminder of your brand—a presence web apps cannot achieve.
Conclusion
Both web apps and native apps play a role in today’s digital landscape, but when it comes to delivering a superior user experience, native apps lead the way. They are faster, more secure, and integrate seamlessly with mobile devices, providing personalization, offline access, and engaging features that web apps simply cannot match.
For businesses aiming to strengthen their digital presence, investing in mobile app development alongside strong web design and web development strategies is the best way forward. By combining these disciplines, companies can build scalable, user-friendly platforms that delight customers and create lasting value.