Back-End Development: A Complete Guide
In today’s technology-driven world, it’s nearly impossible for a business to thrive without a strong digital presence. Alongside this growth, however, comes an increase in web security threats. In fact, 2023 statistics reveal that over 2,000 web security threats occur every day. This makes it crucial for businesses to understand these risks and take proactive steps to protect their digital assets.
This comprehensive guide will explore the most common web security threats, their potential impact on your business, and strategies to identify and prevent them. By integrating secure web development practices and thoughtful web design, you can build websites and applications that not only deliver excellent user experiences but also safeguard sensitive data, ensuring your business remains resilient in the face of cyber threats.
20 Most Common Web Security Threats
Malware
Malware attack is one of the most common web security threats where harmful malware [software] is delivered and installed without the end user’s knowledge to cause harm or damage to the computer, server, client, computer network, or infrastructure. Moreover, it is an umbrella term for various malicious programs including viruses, ransomware, scareware, spyware, adware, worms, trojans, and file-less malware.
- Objective of Malware Attacks: To infiltrate systems, steal data or perform harmful activities.
- Target of Malware Attacks: Usual targets of malware attacks include individuals, organizations, or specific systems.
- Means of Attack: Malware attacks can be performed through infected files, email attachments or harmful software.
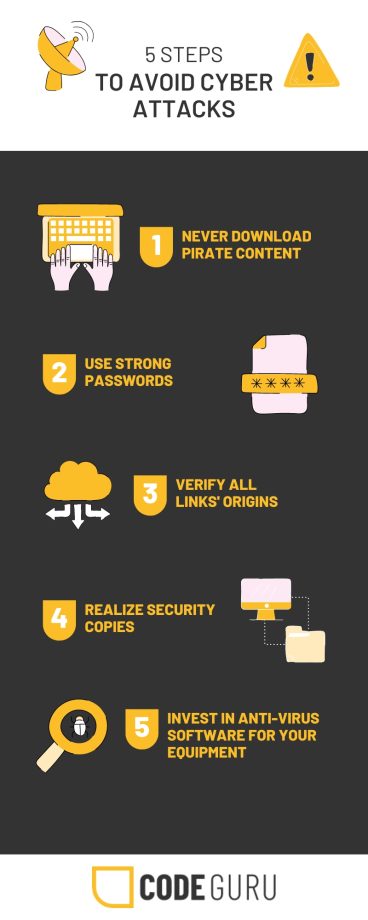
- How to Prevent Malware Attacks: [i] Install antivirus software [ii] Always update software [iii] Be cautious with email attachments [iv] Regularly backup data.
Phishing
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack whereby the attacker impersonates a reputable organization or person in various forms of communication [email, instant message, text message] to trick the victim into sharing personal information. Moreover, by pretending to be someone else and making enticing offers, the attacker lures the victim similar to how a fisherman uses bait to catch fish.
- Objective of Phishing: To deceive individuals into revealing sensitive information.
- Target of Phishing: Usual targets of phishing include individuals or employees within reputable companies.
- Means of Attack: Phishing is performed through deceptive emails or websites posing as trusted sources.
- How to Prevent Phishing: [i] Always verify email senders [ii] Be cautious with email links and attachments [iii] Educate employees about phishing.
Brute Force Attack
A brute force attack is a hacking method whereby the attacker guesses username and login details to gain unauthorized access. In this method of cybercrime, the attacks are done by brute force, meaning they try to forcefully enter the account through rigorous trial-and-error. Although it’s an old form of cyberattack, it’s one of the simplest and most reliable methods among hackers and is gaining popularity again due to an increase in remote work.
- Objective of Brute Force Attack: To gain unauthorized access by guessing passwords or keys.
- Target: Usual targets of brute force attacks are user accounts, encrypted files, or secure systems.
- Means of Attack: Brute Force attack uses automated tools to try numerous combinations.
- How to Prevent Brute Force Attacks: [i] Use strong and unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication [ii] Limit login attempts.
Social Engineering
At its root, social engineering isn’t a cyberattack, instead, it is a broad range of malicious activities that exploits human error to gain access to sensitive information. Social engineering is a skillful combination of persuasion, and manipulation to fool innocent targets. Since social engineering is based on psychology and human errors, it’s also called ‘human hacking.’
- Objective of Social Engineering: To manipulate individuals or organizations to reveal sensitive information.
- Target: Usual targets of social engineering include individuals, employees within organizations, or even entire organizations.
- Means of Attack: Social engineers use a variety of techniques to deceive and instill fear, worry or urgency including phishing, pretexting, impersonation, baiting, and quid pro quo.
- How to Prevent Social Engineering: [i] Verify identity, especially when requesting private information [ii] Use strong authentication [iii] Practice caution online [iv] Double-check requests [v] Educate employees on social engineering.
Botnets Attack
A botnet is a group of compromised devices that are linked together to perform harmful activities. It is controlled by a cybercriminal, or bot-herder in a remote environment. In botnets attack, the hacker injects harmful malware on the device to turn them into ‘zombie bots.’ Such attacks pose a greater threat as it allows the hacker to perform a large number of actions at the same time. Botnet attack is usually carried out for intense scraping, DDoS, and other large-scale cybercrime.
- Objective of Botnet Attack: To launch DDoS attacks, steal data, spread malware, send spam, and other cybercrimes.
- Target: Usual targets of botnet attacks include websites [for DDoS attacks], individual computer users [for data theft or spreading malware], organizations [for data breaches or corporate espionage], and infrastructure components like routers and IoT devices [for network disruption].
- Means of Attack: Botnet attack typically involves compromise [infecting devices with malware], command and control [remotely controlling botnets through command and control server], execution [botnets execute hacker’s commands], and propagation [some botnets have self-propagation abilities whereby they infect other devices on the same network or exploit flaws to spread further].
- How to Prevent Botnet Attacks: [i] Use security software [ii] Regularly update software [iii] Implement network monitoring tools [iv] Configure firewalls [v] Enable strong authentication [vi] Segment critical systems from less critical ones to limit impact [vii] Perform regular security audits and scans [viii] Educate employees and users.
Distributed Denial of Service [DDoS] Attacks
Distributed Denial of Service, also known as a distributed network attack. It is a cyber crime whereby the attacker floods a server with internet traffic to prevent access to legitimate users.
- Objective of DDoS Attacks: To disrupt online services by overwhelming them with traffic.
- Target: The usual targets of DDoS attacks include websites, online services, or network infrastructure.
- Means of Attack: DDoS is deployed by botnets generating massive traffic volumes.
- How to Prevent DDoS Attacks: [i] Use DDoS mitigation services [ii] Configure firewalls [iii] Monitor network traffic for any suspicious activities.
SQL Injection Attacks
SQL injection attack or SQLi is one of the most common cyberattacks. Structured Query Language [SQL] is a language designed to communicate with databases. Since its inception in the 1970s, SQL has become a standard for numerous commercial and open-source databases. In SQLi attacks, the attacker injects harmful SQL queries on databases using specially crafted SQL statements, to retrieve sensitive information. A successful SQL injection can allow the attacker to exploit private data, modify database data [insert/update/delete], execute administrative operations upon the database, recover data, and in some cases, order commands on the operating system.
- Objective of SQLi Attacks: To exploit database vulnerabilities to manipulate or steal data.
- Target: The usual target of SQL attacks is web applications that interact with databases.
- Means of Attack: SQLi attack is deployed by inputting harmful SQL code into input fields.
- How to Prevent SQLi Attacks: [i] Implement input validation system [ii] Use parameterized queries [iii] Always update software.
Cross-Site Scripting [XSS] Attacks
Cross-site scripting, also known as XSS, is a cyberattack whereby the attacker injects harmful scripts to legitimate websites. The script executes as soon as the victim loads the site. It allows the attacker to impersonate a victim user, perform actions that can be done by the user, and access the user’s data. In more technical terms, cross-site scripting is also a client-side code injection attack.
- Objective of XSS Attacks: To steal data, session cookies or perform actions on behalf of the victim without their consent.
- Target: The usual targets of XSS attacks are websites and its users. Any website that allows user-generated content or doesn’t correctly validate input is vulnerable to XSS attack. Additionally, users who visit compromised websites can become victims.
- Means of Attack: XSS attacks occur in several ways including stores XSS, reflected XSS, and DOM-based XSS.
- How to Prevent XSS Attacks: [i] Implement strict input validation [ii] Ecode user-generated content [iii] Use Content Security Policy [USP] headers [iv] Regularly update software [v] Regularly perform security assessments [vi] Use Web Application Firewalls [WAFs] [vii] Educate users on XSS attacks.
Man-In-The-Middle [MITM] Attacks
Man-in-the-Middle or MITM is an eavesdropping or wiretapping attack. It involves the attacker interfering with a conversation or data transfer between two parties and pretending to be either one of the two legitimate participants. The attacker may intercept a conversation between two people, two systems, or one person and a system.
- Objective of MITM Attacks: To interfere or potentially modify communications, to collect sensitive information [login details, baking details], and to convince the victim to perform specific actions [altering login credentials, completing transactions, initiating bank transfers].
- Target: Any network communication.
- Means of Attack: MITM attack can be deployed in several ways including ARP Spoofing, DNS Spoofing, DNS Spoofing, and Rogue Wi-Fi Hotspots.
- How to Prevent MITM Attacks: [i] Use secure and encrypted connections [HTTPS] [ii] Be cautious when connected to unknown networks.
Zero-Day Exploit
Zero-day exploits are one of the most severe types of cyber attacks.
- Objective of Zero-Day Exploit: To take advantage of unknown flaws to gain access.
- Target: Usual targets of zero-day exploits include systems or devices with vulnerable software or hardware.
- Means of Attack: Zero-day exploits are performed by developing or acquiring exploit code.
- How to Prevent Zero-Day Exploit: [i] Regularly apply security patches [ii] Use intrusion detection systems and network segmentation.
Cryptojacking
Cryptojacking or malicious crypto mining, is a cyberattack whereby the hacker hijacks the victim’s device [desktop, laptop, smartphone, and even servers] to illicitly mine for cryptocurrency.
- Objective of Cryptojacking: To generate cryptocurrency profits without the victim’s knowledge or consent.
- Target: The usual targets of cryptojacking are individual computer users; however, organizations and websites can also be affected.
- Means of Attack: Cryptojacking is performed through various methods including harmful scripts, malware, and browser-based mining.
- How to Prevent Cryptojacking: [i] Use ad-blockers [ii] Install and update antivirus software [iii] Regularly update software [iv] Monitor CPU usage [v] Employ strict network security measures [vi] Implement Content Security Police [CSP] headers on website [vii] Educate employees and users.
Wireless Network Security Threats
Such web security threats can harm the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data transferred between wireless networks.
- Objective of Wireless Network Security Threats: To compromise the security of wireless networks or to exploit the flaws in wireless technologies.
- Target: Usual targets of wireless network security threats include home Wi-Fi networks, corporate networks, public Wi-Fi- networks, Bluetooth and NFC devices, and Wireless Access Points [APs].
- Means of Attack: Wireless network security threats can be deployed through several ways including Eavesdropping [sniffing], Rogue Access Points, Denial of Service [DoS] Attacks, Password Cracking, Man-in-the-Middle Attacks, Evil Twin Attacks, Bluetooth Vulnerabilities, NFC Attacks, War Driving, WEP and WPA Cracking, Encryption Protocol Exploitation, Packet Injection, and EAP Attacks.
- How to Prevent Wireless Network Security Attacks: [i] Use strong encryption [ii] Regularly update firmware [iii] Create strong and unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication, when possible [iv] Segment critical systems from less critical ones to limit impact [v] Employ Intrusion Detection Systems [IDS] [vi] Conduct regular security audits.[vii] And finally, educating users on best wireless practices.
Password Guessing
Password guessing is when a hacker attempts to guess users’ usernames and passwords by using information obtained through data breaches. Moreover, the attackers take advantage of this information and attempt to use it across multiple platforms hoping to login to as many online platforms as possible. They seek to exploit data from data breaches on several sites, and they are effective in doing so, especially when users use the same passwords on various networks.
- Objective of password guessing: To gain access to as many accounts as possible using user information obtained from data breaches.
- Target: The usual targets of password guessing involve any group of individuals that have their information leaked through data breaches on any given website.
- How to prevent: [i] Firstly, using weak passwords on several sites is not recommended, such as Facebook and Twitter, might raise the danger of these attacks. [ii] Furthermore, to establish more protection against this sort of attack, web developers propose using stronger passwords that are unique on each platform.
Ransomware
Ransomware is one of the most common web security threats gaining popularity in developed countries. This type of assault is aimed at firms that rely on software to carry out their regular operations. Ransomware requires victims to pay a fee to gain access to their devices. Moreover, the hacker threatens to wipe it entirely.
- Objective of ransomware: To gain complete access to the victim’s computer and encrypt their data so that it’s no longer accessible to the user. For the user to gain access to their data they must pay money to the attacker.
- Target: Ransomware is targeted toward businesses that are dependent on performing their business activities on their electronic devices. They can also be targeted towards individuals if they are infected by the malware.
- Means of attack: This type of attack can be done in several ways but is mostly performed through the internet. When users download files through an unknown source there is a risk that the malware could be downloaded through that. Infected users can also pass on the malware if they connect their infected devices to other devices.
- How to prevent: Ransomware attacks are hard to detect in their early stages and have continued to evolve over the past couple of years. To reduce the risks of this attack web developers recommend focusing on prevention methods which include [i] training your staff. [ii] Additionally, implementing strong security protocols could strengthen the security.
Corporate Account Takeover
Corporate Account Takeover is a type of business entity theft that involves an attacker who tries to impersonate a legitimate business and gain access to that business’s account. The attacker then sends the corporate funds into their account and tries to steal information about the business’s customers to continue the process.
- Objective of Corporate Account Takeover: For attackers to gain access to corporate bank accounts and authorize funds into their accounts. They use this advantage to gain access to the business’s customers’ sensitive information as well.
- Target: Institutions that have weak security safeguards and minimal control of their banking systems are the targets. The target of the attack expands after the attacker gets more information about their customers.
- Means of attack: This type of attack is usually done through malware that is infected onto a computer through email or websites and is disguised onto the computer as legitimate software
- How to prevent: [i] Adding authentication layers to payment methods of businesses such as biometrics is one way of reducing the risks of this attack. [ii] Training employees to be more aware of online security risks. [iii] And lastly, performing monthly security scans should reduce the chances of an attack.
Supply Chain Attacks
A supply chain attack is a type of web security threat that is targeted toward third-party vendors that offer their software and services that are crucial in the supply chain system. Supply chain attacks are dangerous because the software that is compromised by malware has been signed and certified by trusted vendors. Therefore it makes it unlikely for the user to know that the software being downloaded is infected by malware.
- Objective of Supply Chain Attacks: The objective of a supply chain is to infiltrate weak points. They attack the organization’s supply chain to gain access to valuable business resources.
- Target: The usual target involves businesses that are in the financial sector or government sector.
- Means of attack: This type of attack is focused on getting malware into software that has a weaker security protocol. The infected software is then distributed to businesses to which the malware spreads gaining access to sensitive information.
- How to prevent: [i] Conduct due diligence on your software suppliers to ensure that the right security measures are in place by reviewing the security protocols, certifications, and security procedures.
Insider Threats
An insider threat involves an individual who is within an organization and has access to valuable information about the organization. Moreover, insider threats have the potential to cause significant damage to the organization as the individual has access to sensitive information.
- Objective of Insider Threats: There are many reasons for this form of attack which can include greed or malice within the staff of a business.
- Target: The target of an insider threat is usually the sensitive information that is held within an organization
- Means of attack: Insider threats would usually take the form of the insider trying to take confidential information. It can include customer data and financial data for their use or to sell it to competing businesses.
- How to prevent: [i] Organizations must be trained to identify these threats. This will help them identify when data is being manipulated or misused within the organization.
Malvertising
Malvertising takes advantage of normal online advertising by distributing malicious code through legitimate advertising networks. Although it seems like a trustworthy advertisement through pop ads, paid ads, and banners
- The objective of Malvertising: To distribute malware through advertisements. Additionally it is sent to unsuspecting individuals and gain access to their computer network and data.
- Target: Malvertising is usually targeted towards any online visitor who clicks on the attacker’s ad. The attacker can target their ads demographically, geographically, or even by device types.
- Means of attack: Firstly, the attacker creates an advertisement that encourages users to click on it.
- How to prevent: The two most common ways to prevent malvertising is [i] firstly, installing an ad blocker. An ad blocker can stop advertisements from loading onto a webpage. This includes advertisements that have been implemented into the advertising network. [ii]Likewise, another method would be to download a trusted anti-virus. So that it can identify and remove malware in case of any infections.
Advanced Persistent Attack
An APT attack is carefully planned to evade security measures and fly under the radar undetected.
- Objective of APT attacks: The objective of an APT attack involves the attacker staying undetected in a secure network. Also, they do this for an extended period to get as much information as possible.
- Target: The target of an APT attack usually involves large organizations. They target valuable information such as financial data or other sensitive information.
- Means of attack: Firstly, the attackers usually try to send spear-phishing emails. They usually send it to senior employees within an organization in hopes of spreading the malware. Once the organization’s network is infected the attackers gather account information and credentials within the organization. And lastly, they use that information to get access to secure information and steal valuable information from the organization.
- How to prevent: Generally, a web application firewall can reduce the risks of these attacks as it monitors traffic in and out of the web application.
Drive by downloads
- Objective of Drive-by Downloads: The objective of a drive-by download is to infect a user with malware. They use this to gain access to their personal information.
- Target: Drive-by downloads could happen to anyone who ends up on a suspicious website. Anyone who stumbles upon these sites is the target.
- Means of attack: When a user accesses a webpage that is infected it automatically downloads files. They do this without the user knowing. Even links through emails can trigger an automatic download on the victim’s computer.
- How to prevent: Firstly, educating yourself on the latest methods of how this attack is performed can reduce the chances of you being attacked. Moreover, installing web filtering software can also stop malicious websites from automatically downloading files.
Tips to reduce the impact of Web Security Threats