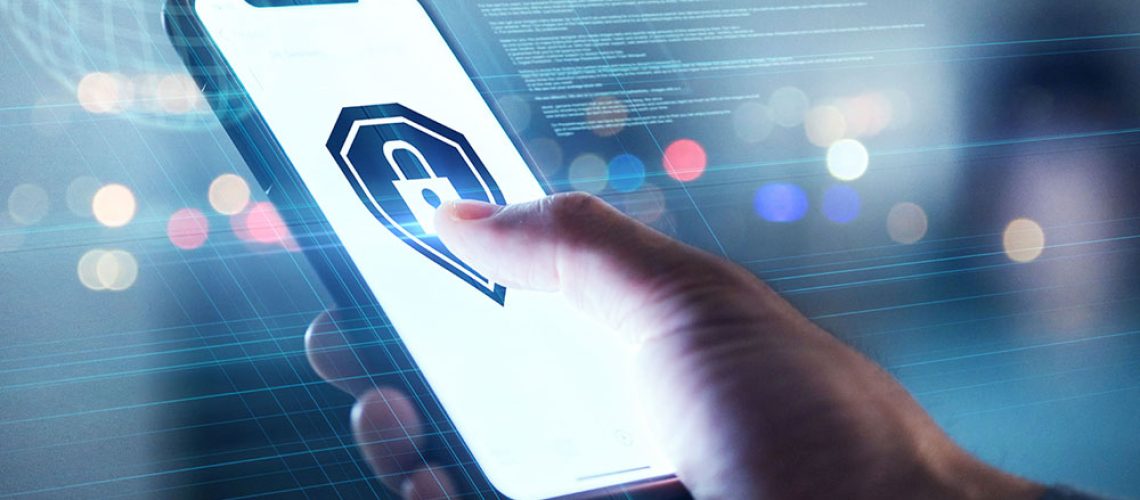
In today’s digital ecosystem, mobile applications have become indispensable tools for businesses and consumers alike. From online shopping and banking to healthcare and communication, apps store and process massive amounts of sensitive data. As a result, security has become one of the most critical aspects of mobile app development. Weak security measures not only put users at risk but also damage brand credibility and trust. That’s why understanding Mobile App Security: Best Practices Developers Must Follow is essential for creating reliable, high-performing applications that withstand modern threats.
While security is often considered a technical component, it plays a vital role across both mobile app development and web development, ensuring consistency and protection across all digital platforms.
Why Mobile App Security Matters More Than Ever
Cyberattacks targeting mobile apps are rapidly increasing. Hackers exploit vulnerabilities to steal data, intercept communications, clone apps, or inject malicious code. Businesses that fail to prioritize mobile security may face financial loss, legal consequences, and long-term reputation damage.
Implementing robust security is no longer optional—it’s a responsibility that every forward-thinking developer must embrace.
1. Use Secure Coding Practices
One of the biggest mistakes developers make is writing code that is easily reverse-engineered or manipulated. Attackers often decompile mobile apps to look for vulnerabilities, weak logic, or hardcoded keys.
How to Protect Your Code
Use code obfuscation techniques to make reverse engineering difficult.
Regularly scan code for vulnerabilities using automated security tools.
Avoid exposing sensitive information in the source code.
Follow established secure coding guidelines for both mobile app development and backend web development services.
Secure coding is the foundation of a safe and trustworthy application.
2. Implement Strong Authentication and Authorization
Weak authentication remains one of the biggest threats to mobile apps. Password-only systems are no longer enough to protect sensitive actions or login credentials.
Best Practices
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
Implement biometrics like fingerprint or facial recognition where appropriate.
Use OAuth 2.0 or token-based authentication for secure communication.
Ensure role-based access control to restrict unauthorized areas of the app.
These methods minimize unauthorized access and strengthen the overall security framework.
3. Use HTTPS and Encrypt All Data
Every interaction between the mobile application and the server must be encrypted. Without encryption, attackers can intercept and read data through Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks.
Essential Measures
Use HTTPS with TLS protocols for all data communication.
Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit.
Implement server certificate pinning to prevent fake certificate intrusions.
Strong encryption is non-negotiable in modern mobile app development.
4. Secure API Endpoints
Mobile apps rely heavily on APIs to fetch data, authenticate users, and perform operations. Weak or exposed APIs are easy entry points for attackers.
How to Secure APIs
Use strong authentication methods before granting access.
Validate and sanitize all inputs to prevent injection attacks.
Limit data exposure by returning only what is necessary.
Monitor APIs with real-time analytics for abnormal activities.
Securing backend APIs is equally critical for both app and web development projects.
5. Avoid Storing Sensitive Data Unnecessarily
Developers should minimize the amount of sensitive information stored on devices. If data is not essential, it should not be stored.
Best Options
Use secure storage mechanisms like encrypted data containers.
Avoid storing passwords or tokens in plain text.
Use Keychain (iOS) and Keystore (Android) for sensitive items.
The less data stored, the smaller the risk.
6. Keep Libraries and Frameworks Updated
Outdated third-party libraries are a silent threat in mobile app development. Many developers overlook updates, leaving known security flaws unpatched.
How to Stay Updated
Track security advisories for third-party frameworks.
Regularly review dependencies and remove unused ones.
Update libraries as soon as security patches are released.
Using only trusted and updated components significantly reduces vulnerabilities.
7. Conduct Regular Security Testing
Security testing must be a continuous process—not a one-time event. With new threats emerging constantly, periodic testing helps identify vulnerabilities early.
Key Testing Methods
Penetration testing
Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
Vulnerability scanning
Code review audits
Regular testing ensures the app stays secure even as new features are introduced.
8. Implement Secure Session Management
Session hijacking is a common security threat targeting mobile apps, especially those involving financial or personal data.
Best Practices
Use short session timeouts.
Ensure tokens expire and cannot be reused.
Store sessions securely, never in plain text.
Proper session management enhances user protection and app integrity.
9. Protect Against Reverse Engineering
Attackers often try to analyze and clone mobile apps. Developers should take steps to make this as difficult as possible.
How to Prevent Cloning and Tampering
Use code obfuscation tools.
Verify app integrity at runtime.
Implement anti-debugging features.
These layers of protection help maintain an app’s authenticity and security.
Conclusion
Understanding Mobile App Security: Best Practices Developers Must Follow is crucial for building high-quality, secure, and trusted applications. As cyber threats evolve, businesses and developers must embrace ongoing protection strategies—from secure coding and encryption to API protection and continuous testing.
Strong security measures are essential not only in mobile app development but also in complementary areas like web development, ensuring a unified and protected digital ecosystem. By following these best practices, developers can safeguard user data, build trust, and deliver apps that stand strong against modern cyber threats.